Aceinna SAEJ1939 protocol¶
The Application Protocol of Aceinna SAE J1939
REVISION HISTORY
| Revision | Date | Author | Description |
| 1.0 | Jan 23, 2017 | Feng | Initial version |
| 1.1 | Apr 20, 2017 | Feng | Updated version upon feedback from customers |
| 1.2 | May 17, 2017 | JF | Formatting |
| 1.3 | Sept 5, 2017 | Feng / JF | Add configuration tables of MTLT user’s guide and Change Name to Aceinna |
| 1.3.1 | Sept 6, 2017 | JF | Updated Packet Rate Divider Table |
| 1.3.2 | Sept 22, 2017 | JF | Update Data format description, New logo. |
| 1.3.3 | Sept 25, 2017 | Feng / JF | Fix typo page 6 |
| 1.3.4 | Mar 15, 2018 | Feng | Change 5.5.1 and 5.5.2 match against firmware |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
5.1 Command and Status Functions
6.1 Non-existence of node address
Introduction
1.1 Purpose
Aceinna J1939 Protocol (AJP) is a communication mechanism used for resolution of the identification of CAN nodes, configuration, and data exchange based upon SAE J1939 and the related standards.
It is a request and reply protocol and communicated within the boundaries of a single CAN network, never routed internetwork nodes. The property places AJP into the layer fourth in Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, but not developed into OSI framework.
1.2 Technical assistance
For assistance or clarification on information in this document, submit a case to Aceinna Inc., www.Aceinna.com
Data Unit Definition
Unit reports data in standard engineering units as shown in following table.
| Data Type | Name | **Scaling ** | Range | **Offset* * | Units |
| Pitch / roll | Degree | 1/32768 | -250 to 252 | -250 | Deg |
| Angular rate | Rate of angular change | 1/128 | -250 to 250.992 | -250 | Deg/s |
| Accelerat ion | Linear accelerat ion | 0.01 | -320 to 322.55 | -320 | m/s² |
TABLE 1: Data Unit Definition
Function Overview
To execute a command the host controller sends a request packet as:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source Address | Host Data Field |
| 6 | 59904 | 234 | 255 | 128-247 |
The data field contains the priority, page and PGN of the function to be executed. The table below summarizes the functions supported and their base PGN.
| Name | Ref | Base PGN | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Get Version | 5.1.1 | 65242 | Requests firmware version from SAE J1939 Node |
| Get ECU ID | 5.1.2 | 64965 | Requests the ECU ID |
| Algorithm Reset | 5.1.3 | 65360 | Resets the state estimation algorithm without reloading fields from EEPROM |
| Save Configuration | 5.1.4 | 65361 | Writes the current configuration into EEPROM |
| Test HW | 5.2.1 | 65362 | Checks the status of the hardware, software and sensors on the specific node |
| Test SW | 5.2.2 | 65363 | |
| Test Status | 5.3 | 65364 | Sets parameters on the specific node. Parameters include: packets to be broadcast; broadcast rate; orientation; accelerometer and rate sensor filter settings; user behavior switches |
| Packet Rate Divider | 5.4.1 | 65365 | Determines the Broadcast Rate |
| Data Packet Type | 5.4.2 | 65366 | Determines the type of packets broadcast |
| Digital Filter | 5.4.3 | 65367 | Set low pass filter for acceleration and rate sensors |
| Orientation | 5.4.4 | 65368 | Allows the orientation to be changed |
| User Behavior Switches | 5.4.5 | 65369 | |
| Acceleration Parameters | 5.4.6 | 65373 | Set acceleration parameters for Extended Kalman Filter |
| PS Setting Bank 0 | 5.5.1 | 65520 | Allows user to change default PS for Bank 0 functions |
| PS Setting Bank 1 | 5.5.2 | 65521 | Allows user to change default PS for Bank 1 functions |
TABLE 2: Function Summary
Packet type
AJP claims two types of packets among J1939 nodes, as control and data message.
AJP supports two types of communication methods as SAE J1939 requests, global and specific.
Global packets may be performed as a sender to all, that all recipients must reply with a global address.
Specific packets may be used to exchange the operations between sender and recipient.
Function Detail
5.1 Command and Status Functions
5.1.1 Version Command:
Type: Global
Host Data Field: 0 Bytes
Host broadcasts a request packet following up SAEJ1939.
Units on the bus respond with PGN message: 0x18FEDASA
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source Address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65242 | 254 | 218 | 128-247 | 5 bytes |
Version Data Field Description
| Byte 0 | Byte 1 | Byte 2 | Byte 3 | Byte 4 |
| Major | Minor | Patch | Stage | Build |
5.1.2 ECU ID Command:
Type: Global
Host Data Field: 0 bytes
Units on the bus respond with message: 0x18FDC5SA*
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 64965 | 253 | 197 | 128-247 | 8 bytes |
Data Field Definition follows up Table 1 of SAE J1939-81.
5.1.3 Algorithm Reset Command:
Type: Specific
Host Data Field: 3 Bytes
Response Data Field: 3 Bytes
PS is Host configurable. See section 5.5
Units on the bus respond with message: 00x18FF50SA (default).
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65360 | 255 | 80 (Default) | 128-247 | 3 bytes |
Data Field Definition
| Byte | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request or response | 0x00 = Request (Host) 0x01 = Response (Unit) |
| 2 | Address of unit being reset | Address of Unit (128- 247) |
| 3 | Success or failure | 0x00 = Failure 0x01 = Success |
5.1.4 Save Configuration Command:
Type: Specific.
Host Data Field: 3 Bytes.
Response Data Field: 3 Bytes.
PS is Host configurable. See section 5.5.
Units on the bus respond with message: 0x18FF51SA (default).
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65361 | 255 | 81 | 128-247 | 3 bytes |
Data Field Definition.
| Byte | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request or response | 0x00 = Request (Host) 0x01 = Response (Unit) |
| 2 | Address of unit being reset | Address of Unit (128- 247) |
| 3 | Success or failure | 0x00 = Failure 0x01 = Success |
5.2 Test Functions:
5.2.1 Hardware bits:
Type: Broadcast
Host sends out a request command.
Response Data Field: 8 Bytes
Units on the bus respond with message: 0x18FF52SA
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65362 | 255 | 82 | 128-247 |
HW Bits Data Field Definition
| Bit | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | masterFail | 0 = normal, 1 = fatal error has occurred |
| 1 | hardwareError | 0 = normal, 1= internal hardware error |
| 2 | Not Defined | |
| 3 | softwareError | 0 = normal, 1 = internal software error |
| 4 | inpPower | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 5 | inpCurrent | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 6 | inpVoltage | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 7 | fiveVolt | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 8 | threeVolt | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 9 | twoVolt | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 10 | twoFiveRef | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 11 | sixVolt | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 12 | grdRef | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
| 13 | pcbTemp | 0 = normal, 1 = out of bounds |
The signals masterFail and hardwareError are controlled by y various systems checks in software that are classified into two categories: hardware and software. Instantaneous soft failures in each of these four categories will trigger these intermediate signals, but will not trigger the masterFail until the persistency conditions are met.
There are three intermediate signals that are used to determine when the masterStatus flag is asserted: hardwareStatus, sensorStatus, and softwareStatus. masterStatus is the logical OR of these intermediate signals. Each of these intermediate signals has a separate field with individual indication flags. Each of these indication flags can be enabled or disabled by the user. Any enabled indication flag will trigger the associated intermediate signal and masterStatus flag.
The hardwareError field contains flag that indicate various types of internal hardware errors.
5.2.2 Software bits:
Type: Specific
Host sends out a request command.
Response Data Field: 1 Byte
Units on the bus respond with message: 0x18FF53SA
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65363 | 255 | 83 | 128-247 |
Software Bits Data Field Definition
| Bit | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | softwareError | 0 = normal, 1 = internal software error |
| 1 | algorithmError | 0 = normal, 1= error |
| 2 | dataError | 0 = normal, 1= error |
| 3 | initialization | 0 = normal, 1 = error during algorithm initialization |
| 4 | overRange | 0 = normal, 1 = fatal sensor over-range |
| 5 | missedNavigationStep | 0 = normal, 1 = deadline missed for navigation |
| 6 | calibrationCRCError | 0 = normal, 1 = incorrect CRC on calibration EEPROM data or data has been compromised by a WE command. |
The softwareError field contains flags that indicate various types of software errors. Each type has an associated message with low level error signals. The softwareError flag in the BITstatus field is the bit-wise OR of algorithm and data error.
The software algorithmError contains flags that indicate various types of software errors and is the bit-wise OR of initialization, overRange and missedNavigationStep.
The software DataError contains flags that indicate low level software data errors, calibrationCRCError.
5.3 Status:
Type: Specific
Host sends out a request command.
Response Data Field: 2 Bytes
Units on the bus respond with message: 0x18FF54SA
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65364 | 255 | 84 | 128-247 |
Software Bits Data Field Definition
| Bit | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | masterStatus | 0 = nominal, 1 = hardware, sensor, com, or software alert |
| 1 | hardwareStatus | 0 = nominal, 1 = programmable alert |
| 2 | softwareStatus | 0 = nominal, 1 = programmable alert |
| 3 | sensorStatus | 0 = nominal, 1 = programmable alert |
| 4 | unlocked1PPS | 0 = not asserted, 1 = asserted |
| 5 | unlockedInternalGPS | 0 = not asserted, 1 = asserted |
| 6 | noDGPS | 0 = DGPS lock, 1 = no DGPS |
| 7 | unlockedEEPROM | 0=locked, WE disabled, 1=unlocked, WE enabled |
| 8 | algorithmInit | 0 = normal, 1 = the algorithm is in initialization mode |
| 9 | highGain | 0 = low gain mode, 1 high gain mode |
| 10 | attitudeOnlyAlgorithm | 0 = navigation state tracking, 1 = attitude only state tracking |
| 11 | turnSwitch | 0 = off, 1 = yaw rate greater than turnSwitch threshold |
| 12 | Sensor overRange | 0 = not asserted, 1 = asserted |
The hardwareStatus field contains flags that indicate various internal hardware conditions and alerts that are not errors or problems and is the bit-wise OR of the logical AND of bit 4 to 7.
The softwareStatus field contains flags that indicate various software conditions and alerts that are not errors or problems and is the bit-wise OR of the logical AND of bit 8 to 11.
The sensorStatus field contains flags that indicate various internal sensor conditions and alerts that are not errors or problems and is bit 12.
5.4 Configure commands:
5.4.1 Packet rate divider:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65365 | 255 | 85 | 128-247 | 2 bytes |
1st byte: destination address
2nd byte is packet rate divider
Packet Rate Divider Field Value Definition
| Byte Value | Packet Broadcast Rate |
| 0 | Quite Mode – No Broadcast |
| 1 | 100 Hz (default) |
| 2 | 50 Hz |
| 4 | 25 Hz |
| 5 | 20 Hz |
| 10 | 10 Hz |
| 20 | 5 Hz |
| 25 | 4 Hz |
| 50 | 2 Hz |
The default PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FF55SA and PS is configurable.
5.4.2 Data packet type:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65366 | 255 | 86 | 128-247 | 2 bytes |
1st byte: destination address
2nd byte: Selects which packets to broadcast
bit 1 – slope sensor, bit 2 – angular rate, bit 3 – accelerometer.
The default PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FF56SA and PS is configurable.
5.4.3 Digital filter:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65367 | 255 | 87 | 128-247 | 3 bytes |
1st byte: destination address
2nd byte is to set low pass cutoff for rate sensors. Cutoff Frequency choices are 5, 10, 20, and 50Hz
3rd byte is to set low pass cutoff for accelerometers. Cutoff Frequency choices are 5, 10, 20, and 50Hz
The default PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FF57SA and PS is configurable.
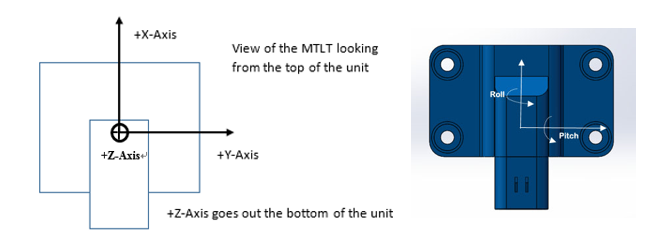
5.4.4 Orientation:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65368 | 255 | 88 | 128-247 | 3 bytes |
1st byte: destination address
2nd and 3rd bytes determine forward, rightward, and downward facing sides
The default PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FF58SA and PS is configurable.
Orientation Field Byte Value Definition
| *Orientation Field Value* | *X Axis* | *Y Axis* | *Z Axis* |
| 0x0000 | +Ux | +Uy | +Uz |
| 0x0009 | -Ux | -Uy | +Uz |
| 0x0023 | -Uy | +Ux | +Uz |
| 0x002A | +Uy | -Ux | +Uz |
| 0x0041 | -Ux | +Uy | -Uz |
| 0x0048 | +Ux | -Uy | -Uz |
| 0x0062 | +Uy | +Ux | -Uz |
| 0x006B | -Uy | -Ux | -Uz |
| 0x0085 | -Uz | +Uy | +Ux |
| 0x008C | +Uz | -Uy | +Ux |
| 0x0092 | +Uy | +Uz | +Ux |
| 0x009B | -Uy | -Uz | +Ux |
| 0x00C4 | +Uz | +Uy | -Ux |
| 0x00CD | -Uz | -Uy | -Ux |
| 0x00D3 | -Uy | +Uz | -Ux |
| 0x00DA | +Uy | -Uz | -Ux |
| 0x0111 | -Ux | +Uz | +Uy |
| 0x0118 | +Ux | -Uz | +Uy |
| 0x0124 | +Uz | +Ux | +Uy |
| 0x012D | -Uz | -Ux | +Uy |
| 0x0150 | +Ux | +Uz | -Uy |
| 0x0159 | -Ux | -Uz | -Uy |
| 0x0165 | -Uz | +Ux | -Uy |
| 0x016C | +Uz | -Ux | -Uy |
Figure: Default Orientation
5.4.5 User behavior switches:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65369 | 255 | 89 | 128-247 |
1st byte: destination address
2nd and 3rd bytes are to set Restart on Over-range and Dynamic Motion.
The default PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FF59SA and PS is configurable
Bit definition for User Behavior Switches
| Bit | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Free Integrate | 0 = use feedback to stabilize the algorithm |
| 1 | Use Mags | 1 = 6DOF inertial integration without stabilized feedback for 60 seconds |
| 2 | Use GPS | N/A |
| 3 | Stationary Yaw Lock | N/A |
| 4 | Restart on Over-range | N/A |
| 5 | Dynamic Motion | 0 = Do not restart the system after a sensor over-range |
5.4.6 Acceleration parameters (optional):
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65373 | 255 | 93 | 128-247 |
1st byte: destination address
2nd to 7th bytes are 16-bit x, y and z acceleration parameters for the EKF coming from host side.
The default PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FF5DSA and PS is configurable.
5.5 Assigning PS Numbers
5.5.1 Bank0 of PS numbers:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65520 | 255 | 240 | 128-247 |
8-byte payload indicates PS numbers instead of default values declared in this doc.
Byte 0: algorithm reset, byte 1: reserved, byte 2: hardware bits, byte 3: software bits, byte 4: status, byte 5–7: reserved.
PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FFF0SA.
5.5.2 Bank1 of PS numbers:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 65521 | 255 | 241 | 128-247 |
Byte 0: packet rate, byte 1: packet type, byte 2: digital filter, byte 3: orientation, byte 4-7: reserved.
PGN message on CAN bus is 0x18FFF1SA.
The pool of PS values should be from decimal 80 to 111.
5.6 Data Packet
5.6.1 Slope sensor information 2:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 61481 | 240 | 41 | 128-247 |
PGN message on CAN bus is 0xCF029SA
The format follows up the definition of slope sensor information 2 in J1939DA_201702.
The first 24-bit indicates pitch and the next 24-bit indicates roll, little-endian.
| SLOT Id | Slot Name | Scaling | Range | Offset | Length |
| 294 | SAEad11 | 1/32768 deg/bit | -250 to 252 deg | -250 deg | 3 bytes |
5.6.2 Angular rate packet:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 61482 | 240 | 42 | 128-247 |
PGN message on CAN bus is 0xCF02ASA
The format follows up the definition of angular rate information in J1939DA_201702.
Each 16 bits indicates the angular velocity (rate) of x, y, z, (little endian).
| SLOT Id | Slot Name | Scaling | Range | Offset | Length |
| 288 | SAEva03 | 1/128 deg/s/bit | -250 to 252 deg/s | -250 deg/s | 2 bytes |
5.6.3 Acceleration sensor packet:
| Priority | Base PGN | PDU format | PDU specific | Source address | Data Field |
| 6 | 61485 | 240 | 45 | 128-247 |
PGN message on CAN bus is 0x8F02DSA
The format follows the definition of acceleration sensor information in J1939DA_201702.
Each 16 bits indicates the acceleration of x, y, z, (little endian), with LSB = 0.01 m/s/s.
| SLOT Id | Slot Name | Scaling | Range | Offset | Length |
| 303 | SAEad11 | 0.01 m/s:sup :2/bit | -320 to 322.55 m/s:sup :2 | –320 m/s:sup :2 | 2 bytes |
Address claiming
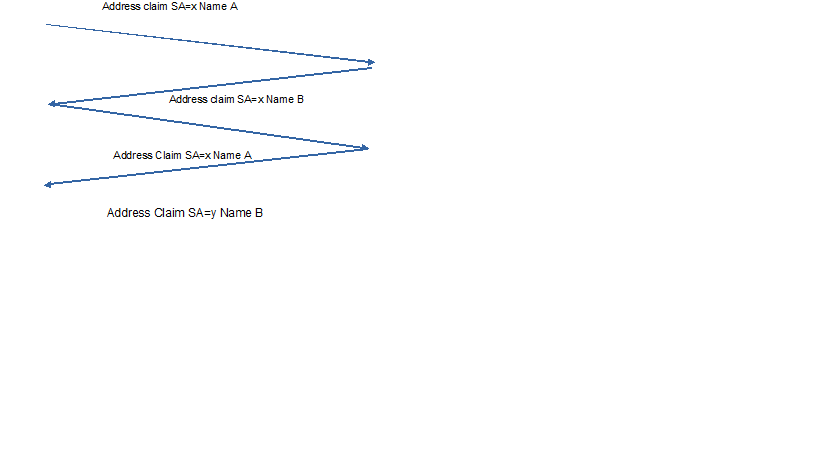
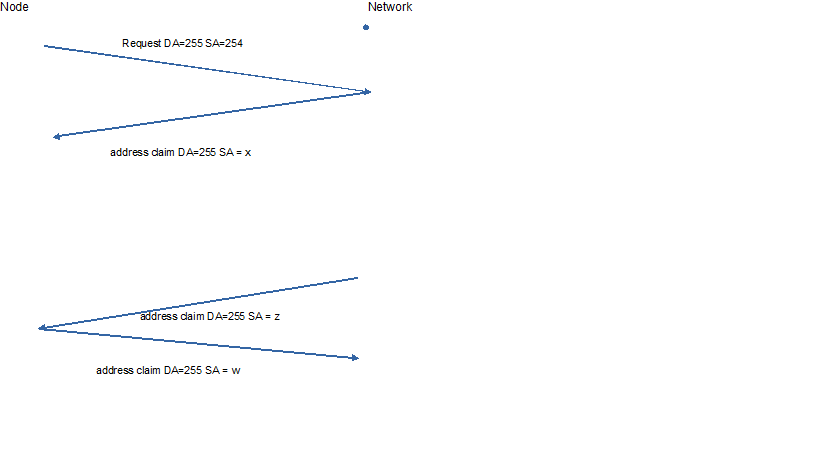
6.1 Non-existence of node address:
The node with null address sends out a global request and waits for the responses from all the nodes on CAN bus. Then, it sends out an address claim message with a chosen address.
6.2 Existence of node address:
The node with an existed address sends out an address claim message and waits for responses from all the nodes on CAN bus, then decides to keep the address or choose next available address.